While Design Thinking (DT) creating a buzz across industries or domains, there is a lot of overwhelming content on popular business magazines like Forbes, HBR, FastCo. etc. reinforcing its importance in businesses. However, there is one common element which everyone wants to stress in Design Thinking is ‘Human Centricity’ or ‘User Centricity’ or a more conclusivily ‘User EMPATHY’. This excites me to write on this topic that whether ‘Empathy’ as an emotion or as an act, really that difficult to inherent Design Led Innovation?
To begin with I tried to build up a scale on Human Emotions + Attitude (Emotitude*) with a scenario around a person who is trying to interact or approach another person.
By ‘interaction’ I mean ‘Talking - setting up a conversation’ or ‘Observing - looking at other’s activities’ or ‘Immersing – participating in his/her activities’.
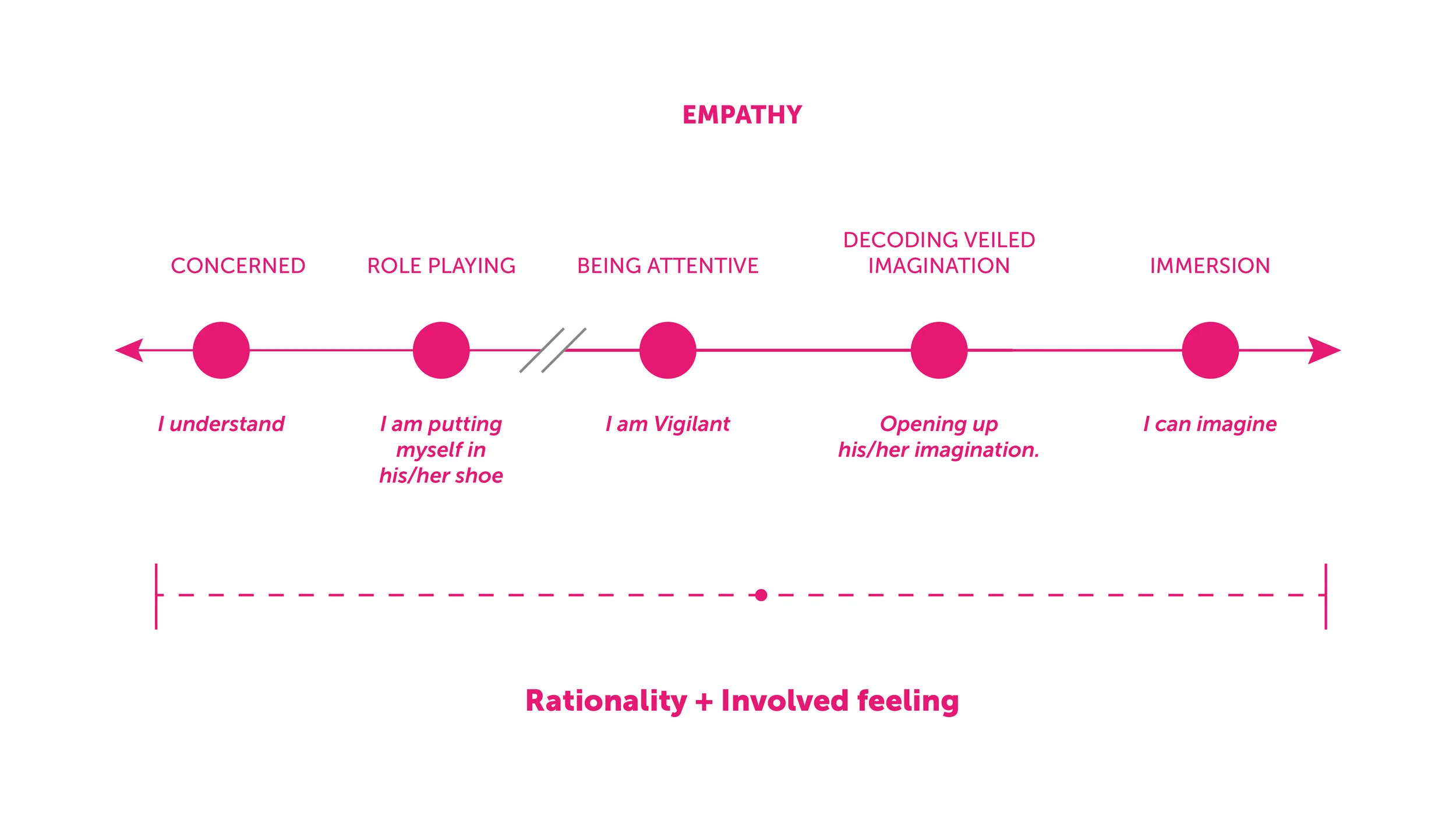
Emotitude* scale
Please note* - This scale is fixed up on a broader emotions along with commonly known acts/attitude which one use in daily lives.
Emotitude scale ranges from a “Don’t bother me” attitude i.e. ‘Ignorant’ emotion to almost feeling helpless for someone (like crying) which could be showing up extreme ‘Sympathy’. As one progresses from being ‘Ignorant’ towards ‘Sympathy’ there is some transition that takes place from being ‘Rational’ to getting ‘Involved in deeper care’. This transition might be extensive with further varied layers, however, I feel this is where ‘Empathy’ lies or takes place broadly.
‘Empathy’ might roughly start from “I understand you” and spread across to a more involved or an immersive emotion of “I can completely imagine your situation”. During this transition one person is trying to rationalise the other person’s situation and at the same time trying to get involved in his/her emotions to ‘Imagine’ or ‘Immerse’. To elaborate this thought, I will further share some regular stories of User research on how ‘Empathy’ played a role from understanding a person to initiate imagination in his / her situation.
Story 1 - Role Play
Background – While carrying out a home visit, I was interacting with a lady who was obstinate in answering my questions. She remained inconspicuous throughout the conversation. Though it was a paid recruitment, she was unable to talk and she only had objective answers. Eventually, I was loosing my patience and had no hopes to get any fruitful insights from this visit. One thing I realised, that she was unwilling to allow me to enter her kitchen for my study purpose.
I somehow got inside and looked around to dig into the scene of her cluttered and messed up kitchen, to know why she was suspiciously reluctant. Here, I tried to put myself in her situation and started imagining why one would have such behaviour. I realised, any woman would have the tendency to hide a messy space in her home! And why? Because the tendency is to avoid getting judged on portraying bad picture of a sacrosanct space like kitchen even if the woman is getting paid for it.
I guess ‘I was right!’. When I started the conversation around her kitchen, she expressed her concern about the muddle and slightly opened up talking about her experiences.
Well, a long story, but few deep dive learning was about user behaviour and how ‘Empathy’ helped to break the barricade of hesitancy.
- Here, I tried to question ‘Why’ to a obvious behaviour, instead of assuming loosely.
- The only way to find the answer was to be like the other person (atleast do a short role play in your mind) and then self analyse.
- Later part was to validate that analysis by probing those questions to the user.
Story 2 - Attentive
Background – Meeting a Quadraplegic Cerebral palacy (Specially abled) girl who was diabetic. To learn how she uses her blood glucose monitoring device on her own.
We tried observing her interaction with the product. We also discussed with her Mother about her experince as a care taker. For a long amount of time we were failing to understand that if at all there was any issue with the device. It is tough to do a role play in such case. We eventually, video recorded this meeting for our later analysis. While repeatedly looking at the video we realised that affordance of her thumb to operate few buttons on the screen was problematic to her, which she was unable to communicate.
We learnt that not always a ‘role play’ or ‘putting yourself in other person’s shoe’ is going to be helpful. Here, ‘being attentive’ or ‘keen’ towards even minor observations can help ‘Empathise’ with the user.
Story 3 – Decode Imagination
Background – In most of communication design projects, we want to learn from user their perception about colors or symbols associated with the brand and it’s attributes.
Such exercises are usually tough to crack. ‘Color’ itself has a lot of individualistic perspective. One person might be in favor of something and the other may have differing opinion.
However, colors or visuals are natural catalyst to grow fruitful conversation with the User. As humans we are visually literate species. Human eye reads a word as picture and sound. Our saccadic vision help in scanning words, recognise them as pictures and immediately trigger its meaning to our brain. And all this happens in fraction of a second. Therefore, the challenge here is to learn what is triggering recognition in the User’s mind.
A set of colors or cards or symbols can help in decoding User’s imagination as User’s tend to talk more what they recognize.
Trick here is to study the pattern of comments made against choices and not the pattern of preferences.
The spectrum of ‘Empathy’ scale itself, has many shades of emotions and attitude one can use towards the User to understand him/her better. Yet, it is a natural asset to everyone of us to simply empathise and learn from the obvious.
Going back to my question “Is Empathy really difficult?” Well, my answer will be it is NOT! But it is Challenging, Demanding and Immersive! Almost like scanning one hundred thousand nuerons sitting inside human neuro system. One has to be extensively passionate to deep dive in the User’s world to really empathise and learn his/her latent needs or wants.
People or organizations who are eager to weave in Design Thinking must learn ‘To Empathise” with their User or collaborate with people who are already fanatical about this subject.
Emotitude* term is coined, for this blog purpose
Please note* - Emotitude scale is completely based on author’s personal hypothesis and may not have a scientific / psychological relevance.
KRANTI VANJARI is a Manager & Subject Expert of Strategy & Design Research at Elephant. She has a graduate diploma in Mechanical Engineering, WCE and a Post Graduate Diploma in Strategic Design for Business, MIT Institute of Design, Pune, India.
Bibliography:
https://think360studio.com/what-is-design-thinking-and-design-thinking-process/
https://www.creativityatwork.com/design-thinking-strategy-for-innovation/
https://www.ideou.com/pages/design-thinking
https://hbr.org/2008/06/design-thinking
https://www.seeker.com/our-brains-see-words-as-pictures-1769641068.html
https://www.childbirthinjuries.com/cerebral-palsy/types/quadriplegic-cerebral-palsy/